How Agentic AI Automates Clinical Trial Analysis and Saves Millions of Dollars
Aug 27, 2025 | 4 min read

What you will get from this guide
Short answer: A simple plan to use agentic AI to draft and test clinical analysis code, keep it compliant, and measure results that leaders care about.
You will learn:
- What agentic AI is, in plain English
- Where it fits in the clinical programming flow
- A safe 90-day pilot plan
- What evidence to keep for auditors
- Why large sponsors like AstraZeneca and Novartis point to real-world readiness
Quick definitions
- Agentic AI: A small team of AI “helpers.” Each helper has a role. One writes code. One writes tests. One checks results. They work together and ask for human help if they are not sure. In a published case, an agentic setup raised first-pass coding accuracy from about 40% to about 93%. Endava
- SDTM (Study Data Tabulation Model): A standard way to structure raw trial data. CDISC
- ADaM (Analysis Data Model): A standard way to structure analysis-ready data that links back to SDTM. The FDA and PMDA expect ADaM for submissions. CDISC
- TLF (Tables, Listings, Figures): The main outputs that appear in a clinical study report.
- GxP: Short for Good Practice rules. GCP is Good Clinical Practice. These rules focus on quality, safety, and strong records. cognidox.comClearDATA
The one-minute overview
Short answer: Agentic AI can draft and self-check clinical code, then give you a clean evidence pack for review. In one real case, first-pass accuracy reached about 93%. Humans still approve the final output. Endava
Why now: Teams must move faster and prove quality at the same time. Agentic AI removes repeatable coding work, so statisticians and programmers focus on design and review. AstraZeneca’s public work with SAS shows sponsors are using AI to speed analysis and submission tasks today. SASPharmaTimes
Who else: Novartis reports that AI has made patient enrollment faster and more efficient. This signals broader readiness to use AI across trial operations. Reuters
Where to use agentic AI first
Short answer: Start where rules are clear and the work repeats from study to study.
- SDTM to ADaM conversions
Agents apply your standard derivations and record each step. This work is rules-based, so it is a safe place to begin. CDISC - TLF code from shells
Agents turn shells into SAS or R code, write unit tests, run them, and attach pass or fail logs. Reviewers see exactly what passed. CDISC - Standards library reuse
The more you standardize macros and derivations, the more code the agents can reuse across studies. This increases speed and consistency. CDISC
Real-world signals:
- AstraZeneca + SAS aim to raise automation and accelerate reporting and submission timelines with AI and analytics. SAS
- Novartis states that AI has made enrollment faster and more efficient. Reuters
Want a clear, compliant path to AI in clinical programming? Book a CI Health AI Strategy Workshop to scope a focused 90-day pilot, define validation gates, and build the evidence pack your auditors expect.
How the workflow looks in practice
Short answer: Read requirements. Draft code. Test. Escalate if unsure. Save evidence.
- Read requirements
The system takes your Statistical Analysis Plan and TLF shells. It also loads your standards library. - Draft code
A code agent writes SAS or R that follows your house rules. - Auto-test
A testing agent creates unit tests for each derivation and each TLF. Another agent runs the tests and checks results against rules or past runs. - Ask for help when needed
A supervisor agent flags a human reviewer if confidence is low or results differ from what you expect. - Package for audit
The system saves prompts, code, test logs, and approvals. That becomes your evidence pack.
Why this matters: In a published example, using several agents to check each other raised first-pass coding accuracy to about 93%. This does not remove human review. It gives reviewers a stronger draft and better evidence. Endava
Compliance that is easy to show
Short answer: Treat the AI like a validated tool and keep a clear record.
Controls you can use now
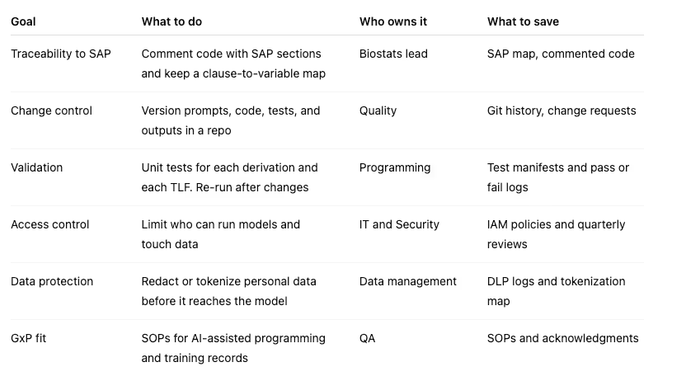
This control set supports GxP goals of quality, safety, and proof that you followed a consistent process. cognidox.comClearDATA
What results to expect
Short answer: Better first drafts, fewer rework loops, and faster cycle time.
- Accuracy: About 93% first-pass coding accuracy reported in a clinical coding use case with agentic AI. Humans still sign off. Endava
- Speed: Public partner statements point to faster reporting and submissions when AI supports analysis. SAS
- Savings: If a sponsor spends $60M a year on programming and validated automation removes 20% of manual effort, that is about $12M saved. Larger portfolios that scale reuse can reach or pass $20M per year. Treat these as planning estimates.
A simple 90-day pilot plan
Short answer: Keep the scope tight. Validate well. Measure everything.
Weeks 1–2: Prepare
- Pick two high-volume TLFs or one SDTM to ADaM flow with clear rules.
- Collect your standards: derivation rules, macro library, and TLF shells.
- Set confidence thresholds. Decide what triggers a human review.
Weeks 3–6: Build and test
- Configure agents for code generation, test creation, test runs, and packaging.
- Run side-by-side with your current process on one finished study to set a baseline.
- Store every test and decision in your repo.
Weeks 7–10: Validate
- Fix gaps. Write SOPs. Train reviewers.
- Run two live studies with the agentic flow. Keep the full evidence pack.
Weeks 11–12: Decide
- Share results and a go or no-go decision with these basics:
Metrics to show
- Time to first draft per TLF
- Rework rate and defects per 100 lines of code
- Percent of code reused from your standards library
- Reviewer approval rate on first pass
Risks and how to keep them small
Short answer: Control inputs, keep PHI out, and never skip tests.
- Data leakage: Do not send personal data to models. Redact names and IDs. Tokenize subject IDs. ClearDATA
- Model error: Keep unit tests for each derivation and each TLF. Require human sign-off for low-confidence outputs. Endava
- Drift over time: Re-validate on known studies at set intervals. Compare outputs to past results.
- Tool lock-in: Keep code portable between SAS and R. Maintain a strong standards library so switching tools is simpler. CDISC
Want a clear, compliant path to AI in clinical programming? Book a CI Health AI Strategy Workshop to scope a focused 90-day pilot, define validation gates, and build the evidence pack your auditors expect.
FAQ
Does this replace programmers?
No. It speeds up repeatable work. People still design the approach, review results, and handle edge cases. Endava
Does 93% mean we can trust every output?
No. It means the first draft is usually close. You still run tests and approve before use. Endava
Why start with SDTM to ADaM and TLFs?
These steps have clear rules and repeat across studies. That makes them safer and more useful for early wins. CDISC+1
Who is doing something similar now?
AstraZeneca and SAS are working together to increase automation in statistical analyses for submissions. Novartis reports AI gains in enrollment. These are strong signals of enterprise readiness. SASPharmaTimesReuters
Conclusion and next step
Agentic AI is ready to help clinical teams write and check more code with less manual effort and clearer evidence. Start small. Standardize your libraries. Validate each step. As confidence grows, expand to more TLFs and more studies. You will see faster analysis, fewer rework loops, and savings that leaders can understand.
Sources
- Endava — Agentic AI in Pharmaceuticals: A Q&A with Richard Pugh
- SAS Newsroom — SAS accelerates delivery of novel medicines using AI and analytics
- PharmaTimes — AstraZeneca and SAS link up on AI and analytics
- Reuters — Insight: Big Pharma bets on AI to speed up clinical trials
- CDISC — ADaM foundational standard
- Allucent — CDISC standards: Guide to CDASH, SDTM, and ADaM
- Sware — What is GxP compliance in the pharmaceutical industry
- ClearDATA — GxP for life sciences



 Gradial
Gradial  PEGA
PEGA